
Worker Protection Standard
Oregon-OSHA Requirements
Division 4, Subdivision W: Worker Protection Standard

Provide emergency assistance.
If a worker or handler has experienced a potential pesticide exposure or shows symptoms of acute exposure within 72 hours after employment and needs medical treatment, employers must do the following:
1. Provide transportation from the workplace (or labor housing) to a medical care facility.
2. Provide the following information to medical personnel for each pesticide product possibly involved in the exposure:
- Product names
- Safety Data Sheets
- EPA Registration Numbers
- Active Ingredients
- Circumstances of application or use of the pesticide
- Circumstances that could have resulted in exposure to the pesticide

Ensure that only employees trained as handlers clean, repair, or adjust pesticide application equipment.
If anyone NOT directly employed by you is to clean, repair, or adjust equipment that has been used for pesticides, employer must provide the following information:
- Application equipment may be contaminated with pesticides.
- The potentially harmful effects of exposure to pesticides.
- Procedures for handling pesticide application equipment and for limiting exposure to pesticide residues.
- Personal hygiene practice and decontamination procedures for preventing pesticide exposures and removing pesticide residues.

Display pesticide safety information and application and hazard information.
This is required if a pesticide product has been used or an REI has been in effect within the last 30 days.

Ensure that pesticide equipment is inspected.
Pesticide equipment should be checked for leaks, clogging and worn/damaged parts and that any damaged equipment is repaired or replaced prior to use.

Keep workers out of restricted areas.
Employers must ensure that workers do not enter a restricted area until the REI has expired and that all treated area warning signs have been removed or covered (except for employees trained as early-entry workers).
All posted information must be displayed where workers and handlers are allowed access to it during normal work hours and must remain legible when displayed.

Content
Note: The following pesticide safety information is included in the Protect Yourself from Pesticides poster. Employers must write the contact information for nearest medical treatment facility and pesticide regulatory agency on the poster.
Pesticide safety information must include:
- Avoid getting on the skin or into the body any pesticides that may be on or in plants, soil, irrigation water, tractors, and other equipment, on used personal protective equipment, or drifting from nearby applications.
- Wash before eating, drinking, using chewing gum or tobacco, or using the toilet.
- Wear work clothing that protects the body from pesticide residues (long-sleeved shirts, long pants, shoes and socks, and hat or scarf).
- Wash or shower with soap and water, shampoo hair, and put on clean clothes after work.
- Wash work clothes separately from other clothes before wearing them again.
- If pesticides are spilled or sprayed on the body use decontamination supplies to wash immediately, or rinse off in the nearest clean water, including springs, streams, lakes or other sources if more readily available than decontamination supplies, as soon as possible, wash or shower with soap and water, shampoo hair, and change into clean clothes.
- Follow direction about keeping out of treated areas and application exclusion zones.
- Seek medical attention as soon as possible if they believe they have been poisoned, injured or made ill by pesticides.
- The name, address, and telephone number of a nearby operating medical care facility capable of providing emergency medical treatment. This information must be clearly identified as emergency medical contact information on the display.
- The name, address, and telephone number of the state pesticide regulatory agency.

Location
Pesticide safety information must be displayed at each of the following sites:
- Central posting location
- Anywhere that decontamination supplies must be provided on the agricultural establishment, but only when the decontamination supplies are located at permanent sites or being provided at locations and in quantities to meet the requirements for 11 or more workers or handlers.

Content
The pesticide application information must include the following for EACH pesticide product applied
- Copy of the Safety Data Sheet
- Name, EPA registration number, and active ingredient of the pesticide product
- Crop or site treated and the location and description of the treated area.
- Date(s) and time(s) the application started and ended
- Duration of the REI for that application

Location
Must be displayed at a place where workers and handlers are likely to pass by or congregate and where it can be readily seen and read. Central posting location is best option for ease of employee access.

Timing
Application information must be displayed no later than 24 hours after the end of the application.
It must be displayed continuously from the beginning of the display period until at least 30 days after the end of the REI, or until workers/handlers are no longer on the establishment (whichever is earlier).

Record Retention
Employer must retain application information for 2 years after the date of the expiration of the REI.

Access to Records
Employee
If an employee (current or former) requests a copy of application or hazard information during the 2-year retention period, employers must provide them with a copy of the records (or access to the records) within 15 days of the receipt. The request may be made verbally or in writing.
If a record has been provided previously without cost to an employee and additional copies are requested, the employer may charge reasonable administrative costs for the additional copies (expenses directly related to searching for records or printing/copying costs).
Medical Personnel
If medical personnel requests access or copies of application records to inform diagnosis or treatment of a worker requests a copy of application during the 2-year retention period, the employer must promptly provide the information requested. The request may be made verbally or in writing.
Designated Representative
If a designated representative requests access or copies of application records during the 2-year retention period on behalf of an employee, the employer must provide the information within 15 days after receiving the request. Requests from designated representatives must be in writing and include the following:
- Name of the employee (or former employee) being represented.
- Description of the specific information being requested, including:
- Dates of employment.
- Date or dates for which the records are requested.
- Type of work conducted by the worker or handler during the period for which the records are requested (i.e., planting, harvesting, applying pesticides, mixing or loading pesticides, etc.).
- Specific application and/or hazard information requested.
- Written statement clearly designating the representative to request pesticide application and hazard information on the employee’s behalf that includes the employee’s printed name and signature, date of designation, and printed name and contact information for the designated representative.
- Where to send the information (mailing address or email address) if the request includes that the information be sent.
If the written request from a designated representative does NOT meet the above requirements, the employer is not required to provide access or copies.
If a record has been provided previously without cost to an employee or their designated representative and additional copies are requested, the employer may charge reasonable administrative costs for the additional copies (expenses directly related to searching for records or printing/copying costs).

Training Frequency
- Workers and handlers must be trained BEFORE performing any task in a treated area where a pesticide product or an REI has been in effect in the last 30 days.
- Each worker must be trained annually, unless they are certified as an applicator of RUPs.

Training Qualifications
- The person who conducts the training must meet one of the following:
- Be designated as a trainer of certified applicators, handlers or workers by EPA or state agency responsible for pesticide enforcement.
- Have completed an EPA-approved pesticide safety train-the-trainer program for trainers of workers.
- Be currently certified as an applicator of restricted-use pesticides.
Training can be provided to workers verbally, from written materials, from videos, or other audio-visual methods. WPS training videos in English and Spanish are available on the CGFG and OR-OSHA websites and YouTube.

Training Recordkeeping
- Employers must maintain training records for 2 years from the date of the training and have a record documenting the training for each employee, including:
- The trained employee’s printed name and signature
- The date of the training
- Which EPA-approved training materials were used.
- The trainer’s name and documentation showing that the trainer met the requirements at the time of training.
- Employer name (required for pesticide handlers only)
- Employers are required to provide a copy of the training record upon request to employees.

Worker Training Content
- Responsibility of agricultural employers to provide workers and handlers with information and protections to reduce pesticide exposures and illnesses in the workplace.
- How to recognize and understand the meaning of posted warning signs used for notifying workers of restrictions and treated areas.
- How to follow directions and/or signs about keeping out of treated areas for REI and application exclusion zones.
- Where and in what forms pesticides may be encountered during work activities, and potential sources of exposure (including residues that may be in plants, soil, tractors, application equipment, used PPE, and drift in the air).
- Potential hazards from toxicity and exposure that pesticides present to workers and their families, including acute and chronic effects, delayed effects, and sensitization.
- Routes through which pesticide can enter the body.
- Signs and symptoms of common types of pesticide poisoning.
- Emergency first aid for pesticide injury or poisonings.
- Routine and emergency decontamination procedures, including emergency eye flushing techniques, and to wash or rinse off immediately in the nearest clean water if pesticides are spilled or sprayed on the body (“clean water” includes springs, streams, lakes, and other sources if more readily available than decontamination supplies). Wash or shower with soap and water, shampoo hair, and change into clean clothes as soon as possible after.
- How and when to obtain emergency medical care.
- Instructions to wear work clothing that protects the body from pesticide residues and wash hands before eating, drinking, using chewing gum or tobacco, or using the toilet, when working in pesticide-treated areas.
- Instructions to wash or shower with soap and water, shampoo hair, and change into clean clothes as soon as possible after working in pesticide-treated areas.
- Information about the potential hazards from pesticide residues on clothing.
- Wash work clothes before wearing them again and wash them separately from other clothes.
- Do not take pesticides or pesticide containers used at work to your home.
- Safety data sheets provide hazard, emergency medical treatment and other information about the pesticides used on the establishment they may come in contact with. The responsibility of agricultural employers to do all of the following:
- Display safety data sheets for all pesticides used on the establishment.
- Provide workers and handlers information about the location of the safety data sheets on the establishment.
- Provide workers and handlers unimpeded access to safety data sheets during normal work hours.
- The rule prohibits agricultural employers from allowing or directing any worker to mix, load or apply pesticides or assist in the application of pesticides unless the worker has been trained as a handler.
- The responsibility of agricultural employers to provide specific information to workers before directing them to perform early-entry activities. Workers must be at least 18 years old to perform early-entry activities.
- Potential hazards to children and pregnant women from pesticide exposure.
- Instructions to keep children and nonworking family members away from pesticide-treated areas.
- Instructions to remove work boots or shoes before entering your home, and remove work clothes and wash or shower before physical contact with children or family members, after working in pesticide-treated areas.
- How to report suspected pesticide use violations to the State or Tribal agency responsible for pesticide enforcement.
- The rule prohibits agricultural employers from intimidating, threatening, coercing, or discriminating against any worker or handler for complying with WPS rules or providing information to enforcement agencies regarding conduct that violates the rules.

Handler Training Content
All of the topics required for workers, AND:
- Information on proper application and use of pesticides.
- Handlers must follow the portions of the label applicable to the safe use of pesticides.
- Format and meaning of information contained on pesticide labels and in labeling applicable to the safe use of the pesticide.
- Need for and appropriate use and removal of all personal protective equipment.
- How to recognize, prevent and provide first aid treatment for heat-related illness.
- Safety requirements for handling, transporting, storing, and disposing of pesticides, including general procedures for spill cleanup.
- Environmental concerns, such as drift, runoff, and wildfire hazards.
- Handlers must not apply pesticides in a manner that results in contact with workers or other persons.
- The responsibility of handler employers to provide handlers with information and protections designed to reduce work-related pesticide exposures and illnesses. This includes providing, cleaning, maintaining, storing, and ensuring proper use of all required PPE; providing decontamination supplies; and providing specific information about pesticide use and labeling information.
- Handlers must suspend a pesticide application if workers or other persons are in the application exclusion zone.
- Handlers must be at least 18 years old.
- The responsibility of handler employers to ensure handlers have received respirator fit-testing, training, and medical evaluation if they are required to wear a respirator by the product labeling.
- The responsibility of agricultural employers to post treated areas as required by this rule.

Information Needed for Handlers
Before any handler performs handler activities with pesticide products, the handler must:
- Read the portions of the label applicable to the safe use of the products, or be informed in a manner they can understand.
- Have access to the product label at all times during handler activities.
- Be aware of requirements for any entry restrictions, AEZs, and REIs that apply.
Before any handler performs handler activities in an area treated with pesticides or had an REI in effect within the last 30 days the handler must be informed of:
- The location of pesticide safety information.
- The location of pesticide application and hazard information.
- The location of decontamination supplies.
During Applications:
- Workers and others on site must not be contacted by pesticides (directly or by drift) unless they are trained and equipped handlers involved in the application.
- Applicators must suspend application if any worker or other person is in the AEZ (other than trained and equipped handlers involved in the application).
- Anyone handling “highly toxic” pesticides that has a skull-and-crossbones symbol on the label must be monitored visually or by voice communication at least every 2 hours.
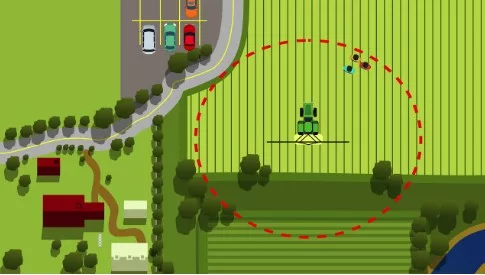
What is the Application Exclusion Zone?
The AEZ is an area surrounding the pesticide equipment that must be free of people (other than handlers/applicators) during pesticide applications. The zone is a circle with a radius of 150 feet, 100 feet, or 25 feet, measured from the equipment. The size of the AEZ is determined by how the pesticide is applied and whether respiratory protection is required for the applicator.
These protections also apply to enclosed structures within an exclusion zone that are occupied at any time by employees or other people. See the AEZ Decision Matrix for determining when an AEZ applies.

Labor Housing & Work-Related Structures in the AEZ
Any structures located within the AEZ must have the following:
- All doors and windows closed.
- Any air in-take device or mechanism turned off.
- Provisions to protect or store personal or household items that are not located inside a structure from potential contamination (barbeques, outdoor toys, etc.)
- A closeable storage area for shoes/boots to prevent tracking of pesticide where people live.

Labor Housing Occupants
Before pesticide application, you must communicate the following to residents affected by the exclusion (including family members and other adult occupants):
- When housing occupants must evacuate and when they are allowed to stay inside.
- When applications are scheduled to start and stop.
- When to close windows and doors (this is required regardless of whether occupants are staying inside or evacuating).
- How to close potential air intakes and take necessary measures to minimize exposure to outside air during the application.
- How long to maintain the protective measures.
- How to prevent contamination of personal or household items within the exclusion zone (such as outdoor furniture, grills, toys, etc.).
- How to recognize and report suspected pesticide residues on or in enclosed structures or on personal items within the exclusion zone.

Access to Information for ALH Occupants
Employers must provide information to all adult occupants of ag labor housing and ensure they have access to:
- Information station located in close proximity to ALH that contains information on pending applications, with a means of alerting occupants to changing information.
- Information on how to prevent and reduce pesticide exposure.
- Information about the location of pesticide safety information.

Notification Requirements
If the product label requires both posting of treated areas and verbal notification to workers, do both.
Otherwise:
- When the REI is equal to or less than 48 hours, verbal notifications OR posted warning signs are required.
- When the REI is great than 48 hours, posted warning signs are required.

Types of Notifications
Verbal Warning Notifications
- Must be provided in a manner workers can understand.
- If workers will be onsite when application begins: warning must be given before the application begins.
- If workers will arrive during application or while REI is in effect: warning must be given when work period begins.
- Verbal notifications must include:
- Location of treated area(s)
- Date(s) and time(s) that entry is restricted to area
- Instructions not to enter the treated area or AEZ during application and REI
Posted Warning Signs
- Signs must be posted prior to the application, but no earlier than 24 hours before it is scheduled to begin.
- Signs must remain posted throughout the application and REI.
- Remove or cover the signs within 3 days after the application ends or REI expires, whichever is later.

Warning Sign Requirements
- Signs must be at least 14 x 16 inches, with letters at least 1 inch in height.
- Sign must be visible from all reasonably expected points of worker entry to the treated area, including at least each access road and each border with any worker housing area within 100 feet of treated area.
- There are specific design requirements for the sign, including background color and required words and images – see WPS rules (Section 170.409) for additional information.
Additional notification and posting requirements apply for applications in enclosed spaces. See WPS rules (section 170.409) for more information.

Definitions
Chemical-Resistant Apron: A chemical-resistant apron that covers the front of the body from mid-chest to the knees.
- If a chemical-resistant suit is substituted for coveralls, then any label requirement for an additional layer of clothing beneath the coveralls is waived.
Chemical-Resistant Footwear: Chemical-resistant boots or shoes, or chemical-resistant shoe coverings worn over shoes or boots.
Chemical-Resistant Headgear: a chemical-resistant hood or chemical-resistant hat with a wide brim.
Chemical-Resistant PPE: Must be made of material that allows no measurable movement of the pesticide through the material during use.
Chemical-Resistant Suit: Loose-fitting, one-piece or two-piece chemical-resistant garment that covers the entire body except head, hands and feet.
Coveralls: Loose-fitting, one-piece or two-piece garment that covers the entire body except head, hands and feet.
- If a chemical-resistant suit is substituted for coveralls, then any label requirement for an additional layer of clothing beneath the coveralls is waived.
Gloves: Must be the type specified on the product label. If no type is specified, then use the category chart to select gloves that will provide the appropriate level of protection.
- Gloves made of leather, cotton, or other absorbent materials may not be worn during handler activities unless they are listed as acceptable on the pesticide label.
- Separable glove liners may be worn beneath chemical-resistant gloves, unless the product label prohibits it.
- Some pesticide labels specify a category for gloves. Download the chart for more information.
Protective Eyewear: Includes goggles, face shield, safety glasses with front, brow and temple protection, and/or full-face respirator.
Separable Glove Liners: Separate glove-like hand coverings, made of lightweight material, with or without fingers. Separable glove liners may not extend outside the chemical-resistant gloves under which they are worn.
- Work gloves made from lightweight cotton or poly-type material are considered to be glove liners if worn beneath chemical-resistant gloves.
- Chemical-resistant gloves with non-separable absorbent lining materials are not allowed.
- Glove liners must be discarded after a total of 10 hours of use or within 24 hours when first put on, whichever comes first.
- Liners must be replaced immediately if directly contacted by pesticides.
- Do not reuse glove liners.
Waterproof: Made of material that allows no measurable movement of water through the material during use.

PPE Requirements
- Handlers must use PPE specified on the product label.
- Employer must provide the handler the PPE required by the product label and ensure the PPE is clean and in proper operating condition.
- Long-sleeved shirts, short-sleeved shirts, long pants, short pants, shoes, and socks are not considered PPE under the WPS rule and therefore does not need to be provided by the employer, although such work clothing must be worn if required by the label.
- When PPE is required, the employer must take measures to prevent heat-related illness.

Use and Maintenance of PPE
- All PPE should be used correctly according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Before each day of use, all PPE should be inspected for damage and wear and repaired or replaced before use.
- All PPE should be cleaned according to manufacturer’s instructions or product labeling instructions before each day of reuse. In the absence of any instructions, PPE should be washed thoroughly in detergent and hot water.
- Contaminated PPE must be kept separate from non-contaminated PPE, other clothing or laundry and washed separately from any other clothing or laundry.

Cleaning PPE
- All washed PPE must be dried thoroughly before being stored or reused.
- All clean PPE must be stored separately from personal clothing and apart from pesticide-contaminated areas.
- Any person who cleans or launders PPE must be informed of the following:
- Such equipment may be contaminated with pesticides and there are potentially harmful effects from exposure to pesticides.
- The correct way(s) to clean PPE and how to protect themselves when handling such equipment.
- Proper decontamination procedures that should be followed after handling contaminated PPE.

Storage of PPE
Handlers must have a place away from pesticide storage and pesticide use areas where they can do the following:
- Store personal clothing not worn during handling activities.
- Put on PPE at the start of any exposure period.
- Remove PPE at the end of the exposure period.
Handlers should not be directed or allowed to take home employer-provided PPE contaminated with pesticides.

Respiratory Protection
Whenever a respirator is required by the product label, the employer must ensure that the respirator specified on the label is used and that requirements of the Respiratory Protection Standard are met.
When a respirator is required, provide the following for handlers and keep records for at least 2 years:
- Medical evaluation to ensure handler can use respirator.
- Annual fit testing to ensure respirator fits correctly.
- Training in proper respirator use, maintenance, cleaning, and storage.
- Replace filters/cartridges/canisters as required
- Particulate Filters: when breathing becomes difficult, filter is damaged, manufacturer or pesticide label requires it, or after 8 hours of use if there are no other instructions available.
- Gas or Vapor-Removing Cartridges: when odor, taste or irritation is present, difficulty breathing, manufacturer or pesticide label requires it, or after 8 hours of use if there are no other instructions available.
Decontamination Supplies for Workers
WHAT DO I PROVIDE FOR WORKERS?
- 1 gallon of water per worker. Water must be of a quality that will not cause illness or injury when it contacts the skin, eyes, or if swallowed and must be cool enough for washing and eye flushing.
- Soap and single-use towels. Hand sanitizer and wet towelettes cannot be substituted.
WHERE DO I PROVIDE DECONTAMINATION SUPPLIES FOR WORKERS?
Supplies must be outside of areas treated with pesticides, but within ¼ mile of all workers.
HOW LONG DO I PROVIDE DECONTAMINATION SUPPLIES FOR WORKERS?
- If the REI is greater than 4 hours, then supplies must be provided when workers first enter treated area and until at least 30 days after the REI expires.
- If the REI is 4 hours or less, then supplies must be provided when workers first enter treated area until at least 7 days after the REI expires.
Decontamination Supplies for Handlers
WHAT DO I PROVIDE FOR HANDLERS?
- 3 gallons of water per handler. Water must be of a quality that will not cause illness or injury when it contacts the skin, eyes, or if swallowed and must be cool enough for washing and eye flushing. Do not use water that is used for mixing pesticides without a backflow-prevention device installed.
- Soap and single-use towels. Hand sanitizer and wet towelettes cannot be substituted.
- Clean coverall or other change of clothing.
- When the label requires protective eyewear, provide at least 1 pint of water per handler in portable containers that is immediately available.
WHERE DO I PROVIDE DECONTAMINATION SUPPLIES FOR HANDLERS?
- Supplies should be kept outside of treated areas, unless they are protected in closed containers.
- Within ¼ mile from the handler, unless handler activity is more than ¼ mile from nearest vehicular access point. In this case, nearest point of vehicular access outside treated area or REI area is acceptable.
- Supplies must be provided at each mixing/loading site. When supplies are inside treated areas, they must be protected in closed containers.
HOW LONG DO I PROVIDE DECONTAMINATION SUPPLIES FOR HANDLERS?
For the duration of the handler activity.

Emergency Eye-Washes
Under WPS rules (Division 4, Subdivision W), when a handler is applying a pesticide product that requires protective eyewear for handlers, at least 1 pint of water or eyewash solution must be provided in portable containers that are immediately available to each handler.
Under Medical/First Aid rules (Division 4, Subdivision K), when handlers are working with products labeled with the signal word “Danger” or “Danger/Poison” AND with a first-aid section on the label that requires rinsing for 15-20 minutes for eye or skin exposure, you must provide an emergency eyewash or shower that is capable of providing rinsing for 15-20 minutes. In this case, the 1 pint of water or eyewash solution is not sufficient.
See Subdivision K (Medical/First Aid) for additional requirements for emergency eyewash or shower.
There are exemptions and exceptions to WPS rules for the owner’s immediate family members and for workers entering treated areas during REIs.

Exemptions for Immediate Family
If the establishment is owned by members of the same immediate family, the owner is not required to provide the following protections to themselves or members of their immediate family when performing handling activities:
Agricultural Employer Duties (Section 170.309(c), and (f) through (j))
(c): Ensure that any handler and any early entry worker is at least 18 years old.
(f): Provide emergency assistance in the event of a suspected pesticide exposure within 72 hours. Provide transportation to medical care facility and provide information to medical personnel (SDSs, product names, EPA registration numbers, active ingredients, circumstances of application and of exposure).
(g): Ensure workers do not clean, repair or adjust pesticide application equipment unless trained as a handler.
(h): Display pesticide safety information and application information.
(i): Ensure that handler is instructed in safe operation of equipment for mixing, loading, transferring or applying pesticides before using any pesticide equipment.
(j): Before each day of use, pesticide equipment is inspected for leaks, clogging, and worn or damaged parts and any damaged equipment is repaired or replaced.
Display Requirements for Pesticide Safety Information and Pesticide Application and Hazard Information (Section 170.311)
Training Requirements for Workers (Section 170.401)
Site-Specific Information for Workers (Section 170.403)
Oral and Posted Notification of Worker Entry Restrictions Section (Section 170.409)
Decontamination Supplies for Workers (Section 170.411)
Decontamination and Eye Flushing Supplies for Handlers (Section 170.509)
Training Requirements for handlers Section (Section 170.501)
Knowledge of Labeling, Application-Specific, and Establishment-Specific Information for Handlers Section (Section 170.503)
Requirements During Applications to Protect Workers, Handlers and Others (Section 170.505(c) and (d))
(c): Handler performing any handler activity with a pesticide product that has the skull-and-crossbones symbol on the front panel of the pesticide product label is monitored visually or by voice communication at least every 2 hours.
(d): Handlers performing fumigant applications in enclosed space product areas maintain continuous visual or voice contact with another handler stationed immediately outside of the enclosed space; handler stationed outside the enclosed space has immediate access to and uses PPE required by the fumigant labeling in the event that entry becomes necessary for rescue.
Personal Protective Equipment (Section 170.507 (c) through (e))
(c): Use of personal protective equipment
(d): Cleaning and maintenance of PPE
(e): Take appropriate measures to prevent heat-related illness when pesticide label requires use of PPE for handlers.
Agricultural Employer Responsibilities to Protect Workers Entering Treated Areas During an REI (Section 170.605(a) through (c), and (e) through (j))
(a): Workers must be at least 18 years old.
(b): Each early entry worker must be provided with information, including pesticides applied, amount of time permitted to remain in the treated area, PPE required for early entry workers, etc.
(c): Early-entry workers must read the pesticide label or be informed of all label requirements prior to early entry.
(e): Maintain PPE in accordance with WPS requirements.
(f): Don’t allow workers to use PPE without implementing measures to prevent heat illness.
(g) Instruct workers on proper use, removal, cleaning, maintenance and disposal of PPE.
(h): Provide decontamination supplies to early-entry workers.
(i): Provide 1 pint of water for eyewash purposes if product label requires protective eyewear.
(j): Provide soap, single-use towels and 3 gallons of water per worker at the end of early-entry activities.

Exceptions for Workers During Re-Entry Intervals
Employers can direct workers to enter treated areas during the REI only under the following conditions:
1. Short-Term Activities
- No hand labor activity is performed.
- Time in treated areas does not exceed 1 hour in any 24-hour period.
- No entry is allowed during the first 4 hours after the application ends.
- Inhalation exposure levels listed in product label have been reached or ventilation criteria have been met.
2. Agricultural Emergencies
- “Emergency” is defined as a sudden occurrence or circumstance that could not have been anticipated and the employer has no control over, that requires entry into a treated area and no alternative practices would prevent or mitigate a substantial economic loss.
- No entry is allowed during the first 4 hours after the application ends regardless of emergency status.
- Inhalation exposure levels listed in product label(s) have been reached or ventilation criteria have been met.
3. Limited Contact and Irrigation Activities
- No hand labor activity is performed.
- No worker is allowed in the treated area for more than 8 hours in a 24-hour period.
- No entry is allowed during the first 4 hours after the application ends.
- Inhalation exposure levels listed in product label have been reached or ventilation criteria have been met.
- The task is one that, if not performed before the REI expires, would cause substantial economic loss and there are no alternatives.
- With the exception of irrigation tasks, the need for the task could not have been foreseen.
- The worker has no contact with pesticide-treated surfaces other than minimal contact with feet, lower legs, hands, and forearms.
- The pesticide product label(s) do not require that workers be notified of the location of treated areas by both posting and oral notification.

Requirements for Workers in Treated Areas During Re-Entry Intervals
If an employer directs workers to perform activities in a treated area while an REI is in effect for any of the above reasons, the following must be done:
- All workers are at least 18 years old.
- Employer provides information orally:
- Location of area where work activities are to be performed.
- Pesticide(s) applied.
- Dates and times the REI begins and ends.
- Which exception is the basis for early entry and a description of tasks performed under the exception.
- Whether contact with treated surfaces is permitted.
- Amount of time the worker is allowed to remain in the treated area.
- PPE required by the product label for early entry.
- Location of pesticide safety information and decontamination supplies.
- Early entry workers have read or been informed of the product label requirements and statements related to human hazards, first aid, and user safety.
- Each worker is provided with the PPE specified in the product label for early entry and instructed in proper use, maintenance, cleaning, and disposal.
- Provide decontamination supplies outside the treated area (unless it is not reasonably accessible, then they can be inside the treated area); if the product label requires protective eyewear, provide one pint of water per worker for eye washing.

Printable Worker Protection Standard Summary
A printable PDF summary of OR-OSHA’s worker protection standard rules.

OR-OSHA Division 4 Rule Text: Worker Protection Standard
Read OR-OSHA’s Division 4 rules about the worker protection standard.


Protect Yourself from Pesticides Poster (bilingual)
Any agricultural operation subject to the worker protection standard is required to have this poster displayed.
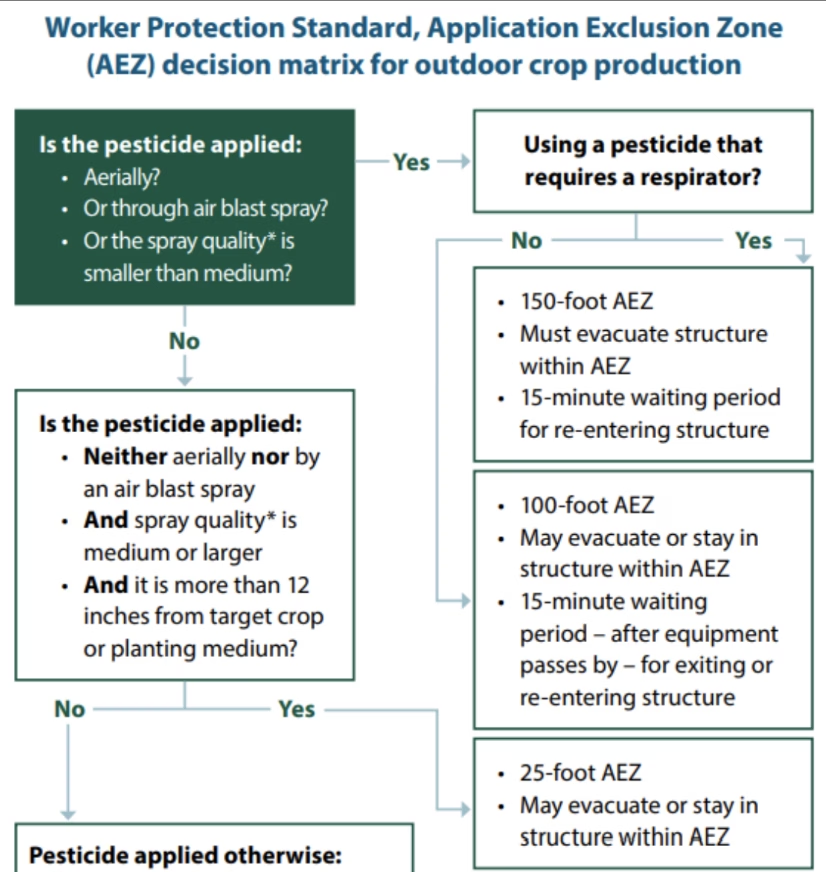
AEZ Decision Matrix
Which AEZ rules do you need to follow? Use this decision matrix to determine how large the AEZ needs to be.

Overview of AEZ Rules
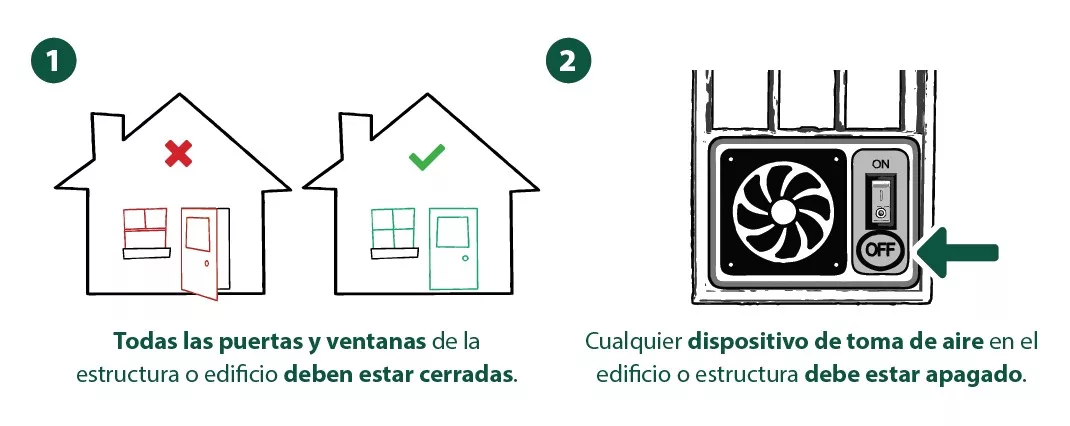
AEZ Rules for Housing & Buildings
A simple guide with illustrations of how to protect people inside buildings and housing within the AEZ.
WPS Train-the-Trainer Online Course
Successful completion of this course certifies you to provide Worker Protection Standard training if you do not have a valid pesticide applicators’ license.
This web-based course is EPA-approved and includes 12 self-paced learning modules. Available in English and Spanish.
The course takes approximately 2-3 hours to complete. After passing the final exam with a score of 70% of better you will be issued a certification.
There is a one-time fee to take the course.


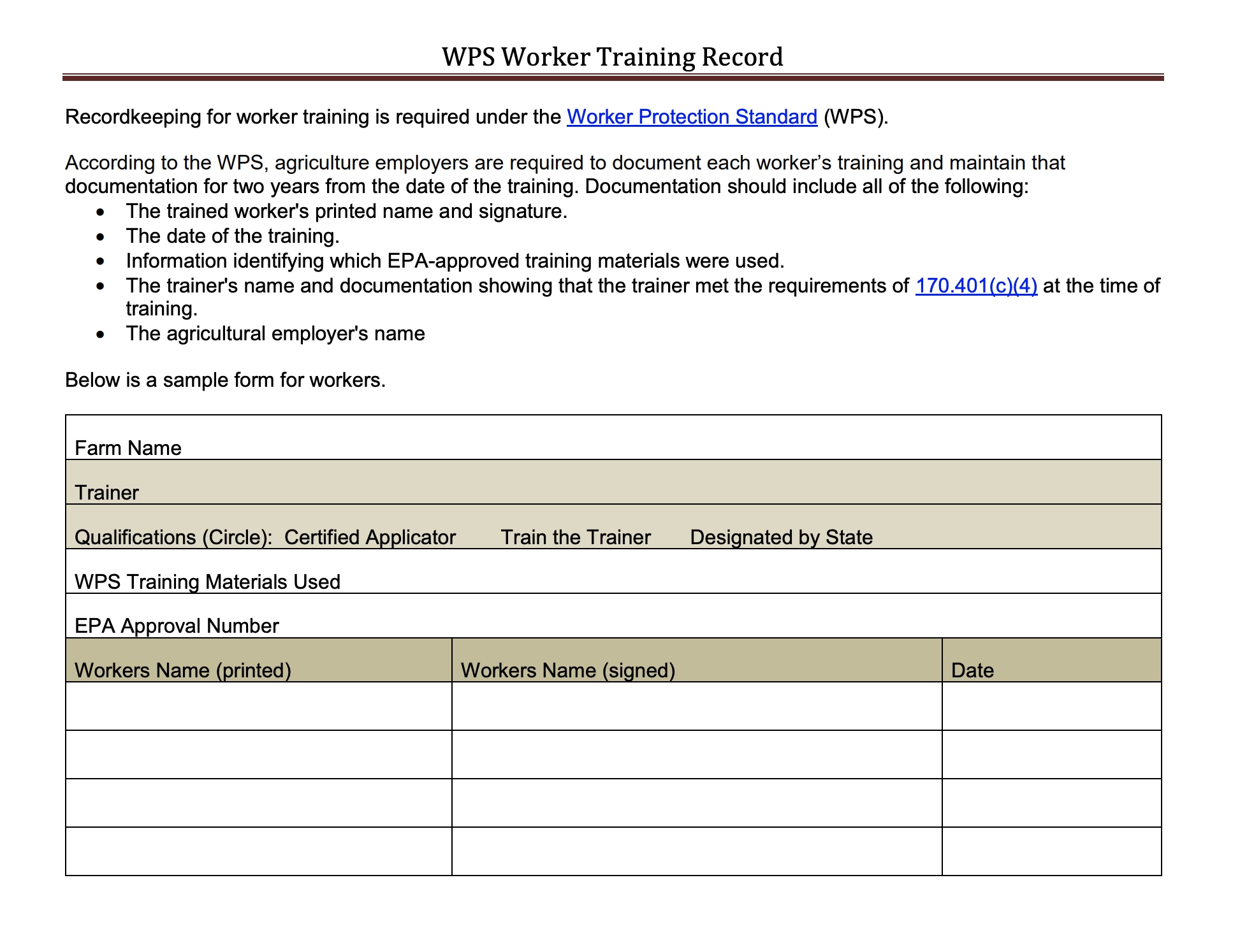
WPS Worker Training Record
Recordkeeping for worker training is required under the Worker Protection Standard.
WPS Training Videos for Workers and Handlers
PERC library of WPS training videos for nurseries, orchards, vineyards, greenhouses, etc.

WPS Video - Workers (English)
This is an EPA-approved video for training WORKERS in English.
(EPA Worker PST 00026; 22 minutes long)

WPS Video - Workers (Spanish)
This is an EPA-approved video for training WORKERS in Spanish.
(EPA Worker PST 00026; 26 minutes long)

WPS Video - Handlers (English)
This is an EPA-approved video for training HANDLERS in English.
(EPA Worker PST 00027; 46 minutes long)

WPS Video - Handlers (Spanish)
This is an EPA-approved video for training HANDLERS in Spanish.
(EPA Worker PST 00027; 57 minutes long)

Purchase WPS Compliance Products
EPA-approved materials available for download or purchase.

WPS Assistance Library (PERC)
This is an educational resource collection by PERC and US EPA’s Office of Pesticide Programs to aid compliance with WPS in agricultural establishments, including farms, orchards, forests, greenhouses, production facilities, and nurseries.
