
These rules apply generally to powered industrial trucks, including forklifts, platform lift trucks, motorized hand trucks, and other specialized industrial trucks used in agriculture.
These are considered vehicles and additional standards are found in Division 4, Subdivision U (Vehicles).
Develop and use a training program for operators of powered industrial trucks. The employer or an outside training entity may give the training. All parts of the training must be tailored to the specific type of equipment, the material being handled, and the location of use. Once fully trained, workers may operate powered industrial trucks.
Training Frequency
Conduct refresher training for drivers annually or when their driving record indicates the need for additional training, whichever is more frequent.
Training Documentation
No training documentation is required.
Training Content
Training must include at least the following:
- Study and Test Portion:
- The rules of the OR-OSHA standard
- Information provided by the manufacturer for operating the equipment correctly
- Any special information dictated by the operating environment.
- Behind-the-Wheel Driving Portion:
- Must be supervised by a person competent in the operation of the equipment.
New Workers
Employers may NOT consider a new worker trained and qualified based on experience from a previous employer unless that experience was the same type of equipment under very similar operating circumstances and the worker had a safe operating record acceptable to the new employer.
- Do not drive up to anyone standing in front of a fixed object.
- Do not pass under the elevated forks/platform.
- Only the operator may ride on the powered truck unless it has a second seat or area intended for another rider.
- Do not put any part of the body between or reach through the uprights of the mast or outside the running lines of the truck.
- Unattended means the operator is 25+ feet away but the vehicle remains in view; or, anytime the vehicle is not in view.
- When the truck is unattended: fully lower forks or platform, neutralize controls, turn off power, set brakes. Block wheels if it is on an incline.
- When the operator is off the truck but within 25 feet and still in view, forks/platform must be lowered, controls in neutral, and brakes set.
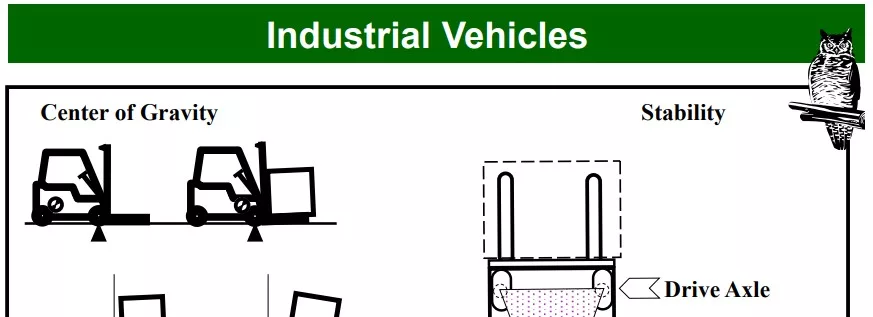
- Climb or descend grades slowly: Drive loaded trucks with the load upgrade if incline is steep enough to spill the load; tilt the load back and raise forks or platform only as far as necessary to clear the road surface.
- Drive only as fast as conditions permit, leaving enough time to stop.
- Slow down on wet and slippery surfaces.
- Do not run over loose objects.
- Do not handle loads heavier than the rated capacity of the truck.
- The forks/platform must be under the load as far as possible and the mast tilted backward to stabilize the load.
- Do not tilt forward with forks/platforms elevated except to pick up a load.
- If a truck needs repair, take it out of service until repairs are complete.
- Do not add fuel when the engine is running.
- Clean up spilled oil or fuel and allow it to completely evaporate before restarting the engine.
- Do not use the vehicle without the fuel filler cap in place.
- Do not use a flame to check the electrolyte level in batteries or level in fuel tanks.
- Only authorized persons may repair powered industrial trucks.
- Disconnect the battery before working on the electrical system.
- Use only replacement parts that assure equivalent safety as the originals.
- Do not add counter weighting to fork trucks without approval by the manufacturer.
- Check trucks daily before using them.
- Remove from service any vehicle that gives off hazardous sparks or flames.
- Keep trucks clean, free of excess oil and grease.
- Clean trucks with noncombustible cleaners. Follow directions on the cleaner’s label.
- You may convert powered industrial trucks from gasoline to liquefied petroleum gas fuel if the converted truck complies with the specifications for LP or LPG trucks. Use only approved conversion equipment.
Included in Subdivision U: Roll-Over Protective Structures – Industrial Vehicles (437-004-3650)
ROPS requirements apply to industrial vehicles that are rubber-tired self-propelled scrapers, front-end loaders and dozers, wheel-type industrial tractors, crawler tractors, crawler-type loaders, and motor graders, with or without attachments.
This requirement does not apply to side boom pipe laying tractors, or other vehicles whose structure prevents overturn. ROPS requirements include general requirements, repairs to defects, and information that should be affixed to the structure.
Controls that Elevate with the Carriage
When a truck has vertical and/or horizontal controls that elevate WITH the lifting carriage or forks for lifting personnel, do the following:
- Use a safety platform secured to the lifting carriage or forks.
- Have a way for people on the platform to shut off power to the truck.
- Provide protection from falling objects as necessary by the operating conditions.
Using Forklift to Lift People
When using a forklift to lift people, take the following precautions:
- Use a platform with standard guardrails secured to the lifting carriage or forks.
- The hydraulic system must not be able to drop faster than 135 feet per minute if any part of the system fails.
- Someone must be in the operator’s station while workers are on the platform.
- Someone must be in the normal operating position while raising or lowering the platform.
- Other than very slow inching, do not move the truck from point-to-point with the platform raised more than 4 feet while workers are on it.
- There must be a guard on the area between the platform and mast to prevent contact with chains or other shear points.
Overhead Guards
- If a lift truck operator could be struck by falling, or stacked objects, the truck must have an overhead guard. The guard must be strong enough to support impact load tests following specific measurements.
- Additional construction standards for canopy guards apply; see Standard 437-004-1700 for more information.
- Guards must not interfere with good visibility.
- Guards must be large enough to extend over the operator under all normal circumstances of operation.
Back Rest
- Lift trucks that handle small objects or loose units must have a vertical load backrest.
- Back rest must not interfere with good visibility.
Shear Point Guards
- Shear points on forklift loaders must have guards.
Fuel Handling and Storage
For additional information about storing and handling liquid fuels and liquid petroleum gas fuel, see Subdivision H: Hazardous Materials (Flammable Liquids, 437-004-0720; Storage and Handling of Liquified Petroleum Gases, 437-004-0780).
Changing and Charging Storage Batteries
- There must be facilities for flushing and neutralizing spilled electrolyte, for fire protection, for protecting charging apparatus and for adequate ventilation.
- Use a conveyer, hoist or other handling equipment to handle large batteries that power electric forklifts.
- Pour acid into water, not water into acid when servicing batteries.
- Set truck brakes before changing or charging batteries.
- Vent caps must function and battery compartment covers must be open to dissipate heat.
- No smoking in the charging area.
- Prevent open flames, sparks or electrical arcs in battery charging areas.
- Keep tools and other metallic objects away from the top of uncovered batteries.

OR-OSHA Division 4 Rule Text: Forklifts
Read OR-OSHA’s Division 4 rules about forklifts.
Bilingual Forklift Information Sheet
Read OR-OSHA’s forklift information sheet for the basics of operating a forklift safely.

OSHA QuickCard: Safe Forklift Operation
Federal OSHA QuickCard resource for safe forklift operation.

OSHA Forklift E-Tool
Federal OSHA resources for powered industrial truck requirements, including types adn fundamentals of forklifts, operating the forklift, and training assistance.

